Java-Web
Java系列之JavaWeb
一、基本概念
1.前言
web开发:
web,网页的意思 , www.baidu.com
静态web
- html,css
- 提供给所有人看的数据始终不会发生变化!
动态web
- 淘宝,几乎是所有的网站;
- 提供给所有人看的数据始终会发生变化,每个人在不同的时间,不同的地点看到的信息各不相同!
- 技术栈:Servlet/JSP,ASP,PHP。
在Java中,动态web资源开发的技术统称为JavaWeb。
2.web应用程序
web应用程序:可以提供浏览器访问的程序。
a.html.b.html……多个web资源,这些web资源可以被外界访问,对外界提供服务。
我们能访问到的任何一个页面或者资源,都存在于这个世界的某一个角落的计算机上。
URL
这些统一的web资源会被放在同一个文件夹下,web应用程序–>Tomcat:服务器。
一个web应用由多部分组成 (静态web,动态web)。
- html,css,js
- jsp,servlet
- Java程序
- jar包
- 配置文件 (Properties)
web应用程序编写完毕后,若想提供给外界访问:需要一个服务器来统一管理;
3.静态web
- *.htm, *.html,这些都是网页的后缀,如果服务器上一直存在这些东西,我们就可以直接进行读取。通络;
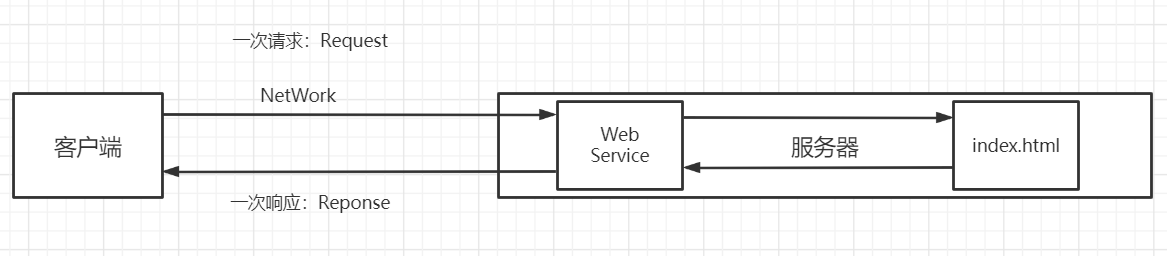 静态web存在的缺点:
静态web存在的缺点:
- Web页面无法动态更新,所有用户看到都是同一个页面;
- 轮播图,点击特效:伪动态;
- JavaScript [实际开发中,它用的最多];
- VBScript;
- 它无法和数据库交互(数据无法持久化,用户无法交互)。
4.动态web
页面会动态展示: “Web的页面展示的效果因人而异”;
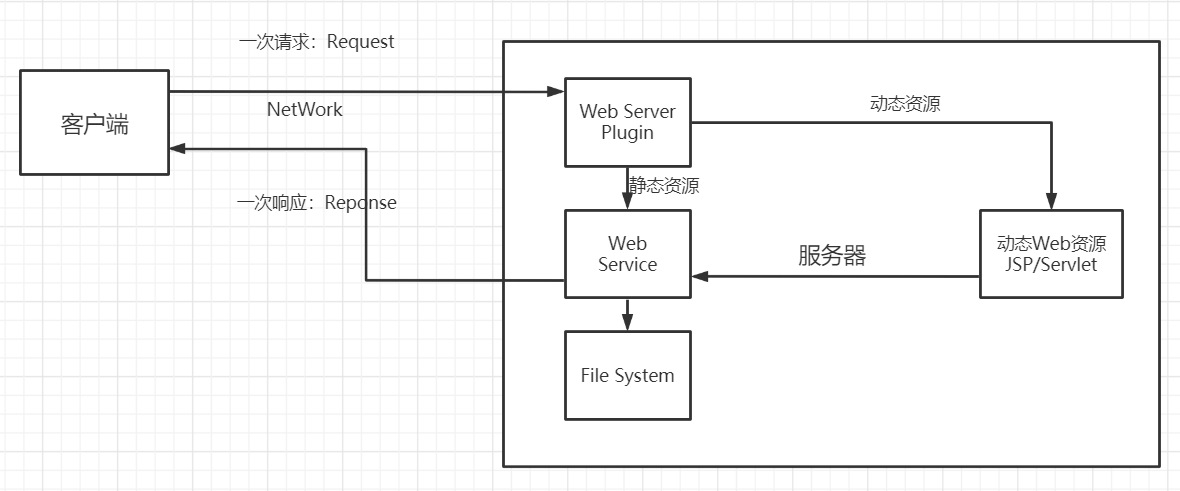
当代项目基本上都是动态页面了,很少有纯静态的了。
缺点:
- 加入服务器的动态web资源出现了错误,需要重新编写后台程序,重新发布;
- 停机维护。
优点:
- Web页面可以动态更新,所有用户看到都不是同一个页面;
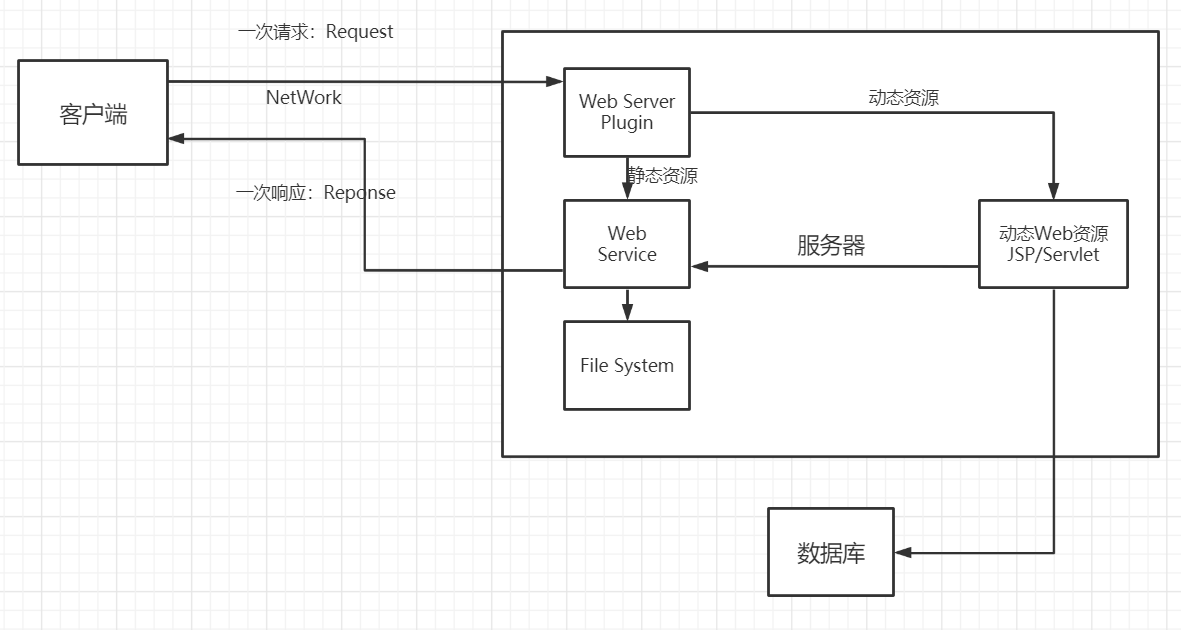
- 它可以与数据库交互 (数据持久化:注册,商品信息,用户信息……..);
二、web服务器
1.技术讲解
ASP:
微软:国内最早流行的就是ASP;
在HTML中嵌入了VB的脚本, ASP + COM;
在ASP开发中,基本一个页面都有几千行的业务代码,页面极其换乱,维护成本高!
C#
IIS
1 | <h1> |
php:
- PHP开发速度很快,功能很强大,跨平台,代码很简单 (70% , WP)
- 无法承载大访问量的情况(局限性)
**JSP/Servlet : **
JSP当下也基本上很少用到了,现时代主流的更多都是前后端分离!
B/S:浏览和服务器
C/S: 客户端和服务器
- sun公司主推的B/S架构
- 基于Java语言的 (所有的大公司,或者一些开源的组件,都是用Java写的)
- 可以承载三高问题带来的影响;
- 语法像ASP , ASP–>JSP , 加强市场强度;
…..
2.web服务器
服务器是一种被动的操作,用来处理用户的一些请求和给用户一些响应信息;
IIS(基本已经淘汰)
- 微软的; ASP…,Windows中自带的
- 更多主要是在内网中可能会有稍微多点
Tomcat

==面向百度编程==;
Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,最新的Servlet 和JSP 规范总是能在Tomcat 中得到体现,因为Tomcat 技术先进.性能稳定,而且免费,因而深受Java 爱好者的喜爱并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,成为目前比较流行的Web 应用服务器。
Tomcat 服务器是一个免费的开放源代码的Web 应用服务器,属于轻量级应用服务器,在中小型系统和并发访问用户不是很多的场合下被普遍使用,是开发和调试JSP 程序的首选。对于一个Java初学web的人来说,它是最佳的选择。
Tomcat 实际上运行JSP 页面和Servlet。Tomcat最新版本为9.0。
….
有能力的时候可以尝试一下手写Tomcat服务器
下载tomcat:
安装 or 解压;
了解配置文件及目录结构;
这个东西的作用。
三、Tomcat
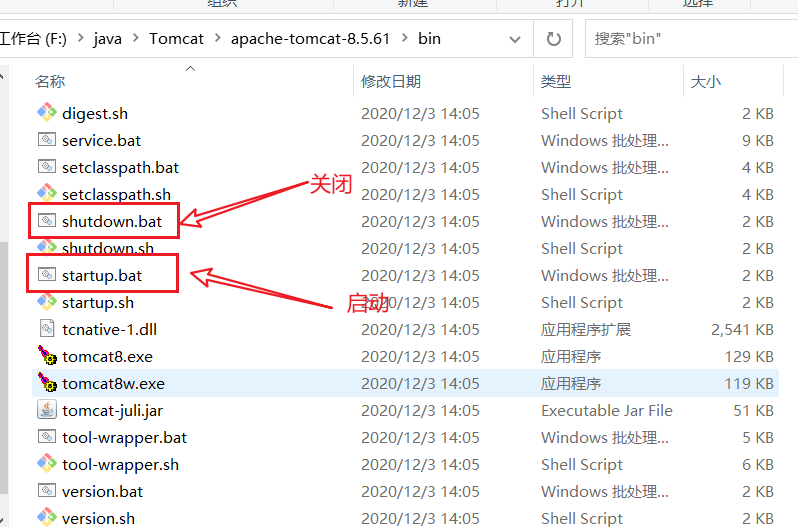
1、Tomcat快速开始
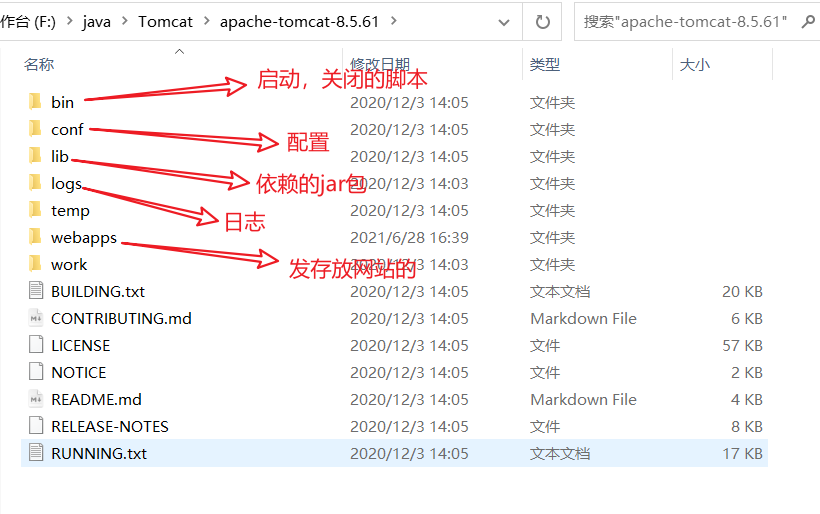
- 启动。关闭Tomcat
2、配置文件修改
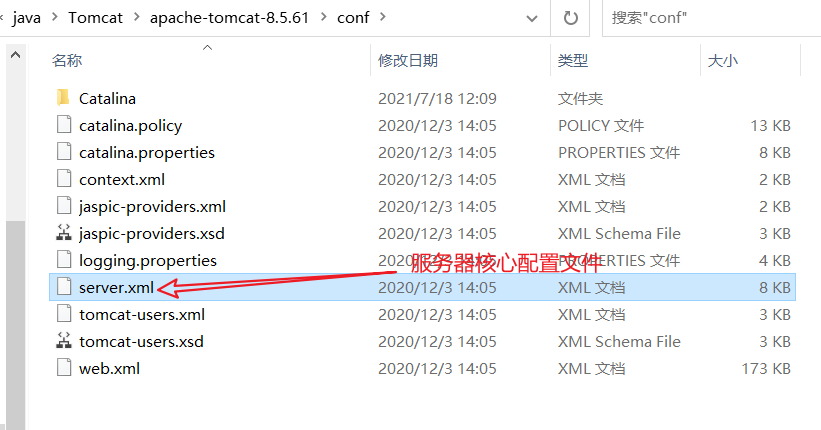
还有就是一些其他的配置文件
比如tomcat-users是用来配置后台登录的
web.xml是用来配置一些比如首页是什么的
3、发布一个Web网站
不会就先模仿:
- 将自己写的网站,放到服务器(Tomcat)中指定的web应用的文件夹(webapps)下,就可以访问了。
网站应该有的结构
1 | --webapps :Tomcat服务器的web目录 |
四、Servlet
1.Servlet简介
Servlet就是sun公司开发动态web的一门技术。
Sun在这些API中提供一个接口叫做:Servlet,如果你想开发一个Servlet程序,只需要完成两个小步骤:
- 编写一个类,实现Servlet接口。
- 把开发好的Java类部署到web服务器中。
把实现了Servlet接口的Java程序叫做,Servlet。
直接可以创建javaweb项目
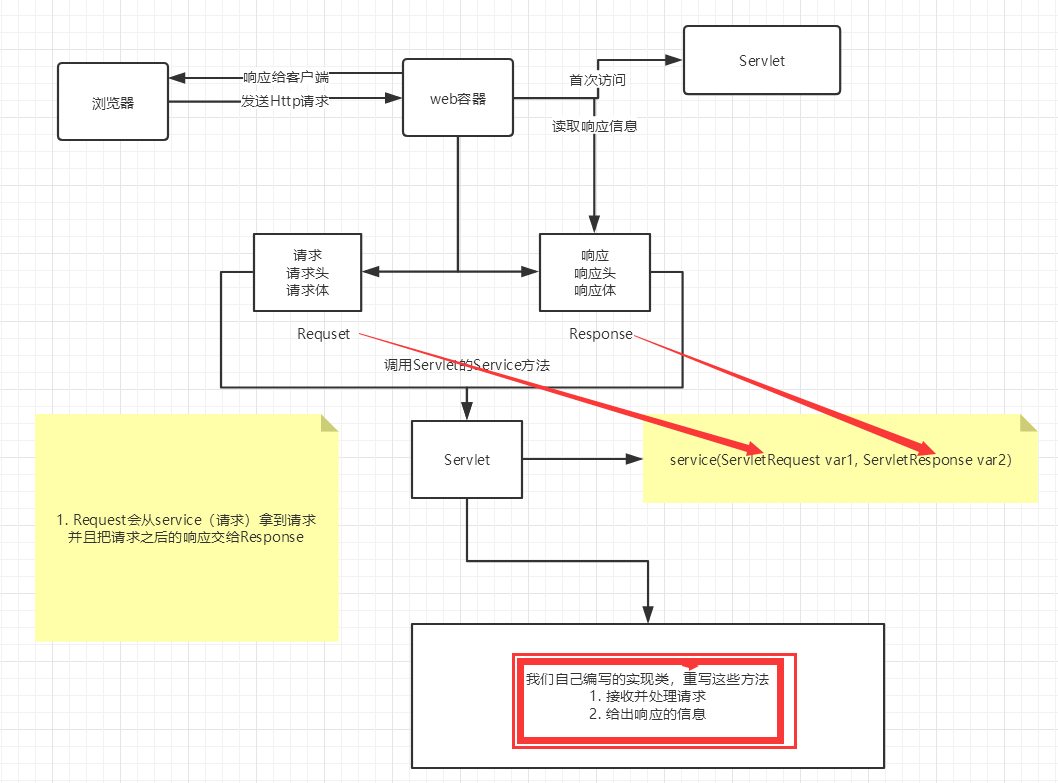
2、Serlvet原理
- Servlet是由Web服务器调用,web服务器在收到浏览器请求之后,会:
3.Mapping问题
一个Servlet可以指定一个映射路径。
1
2
3
4<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>一个Servlet可以指定多个映射路径。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello3</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello4</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello5</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>一个Servlet可以指定通用映射路径。
1
2
3
4<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>默认请求路径。
1
2
3
4
5<!--默认请求路径-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>指定一些后缀或者前缀等等….
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8<!-- 可以自定义后缀实现请求映射
注意点,*前面不能加项目映射的路径
hello/subei.github
-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.github</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>优先级问题。
- 指定了固有的映射路径优先级最高,如果找不到就会走默认的处理请求;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23package com.github.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class ErrorServelt extends HelloServlet{
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();
writer.println("<h1>404</h1>");
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.doPost(req, resp);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9<!-- 404 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>error</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.github.servlet.ErrorServelt</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>error</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
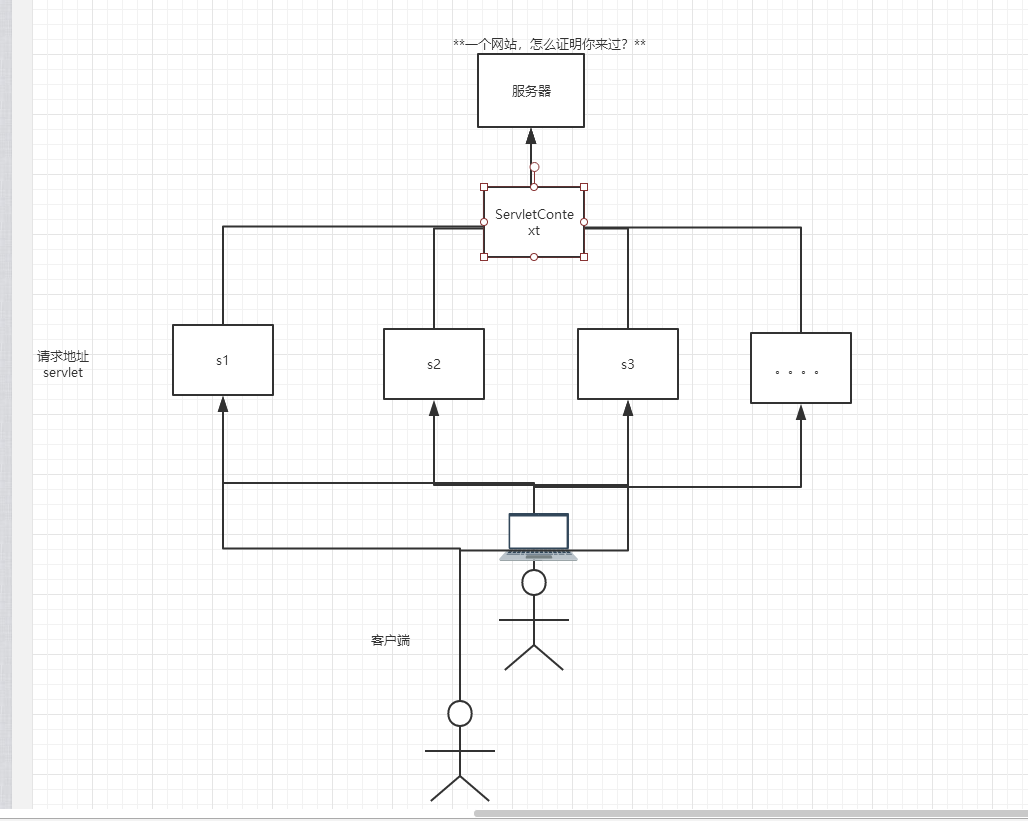
4.ServletContext
- web容器在启动的时候,它会为每个web程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表了当前的web应用;
1.共享数据
- 在这个Servlet中保存的数据,可以在另外一个servlet中拿到;
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
2.获取初始化参数
1 | <!-- 配置一些Web应用初始化参数 --> |
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
3.请求转发
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
4.读取资源文件
- Properties
- 在java目录下新建properties
- 在resources目录下新建properties
5.HttpServletResponse
- web服务器接收到客户端的http请求,针对这个请求,分别创建一个代表请求的HttpServletRequest对象,代表响应的一个HttpServletResponse;
- 如果要获取客户端请求过来的参数:找HttpServletRequest;
- 如果要给客户端响应一些信息:找HttpServletResponse。
1.简单分类
- 负责向浏览器发送数据的方法。
1 | ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException; |
- 负责向浏览器发送响应头的方法。
1 | void setCharacterEncoding(String var1); |
- 响应的状态码。
1 | int SC_CONTINUE = 100; |
2.下载文件
- 向浏览器输出消息;
- 下载文件:
- 要获取下载文件的路径;
- 下载的文件名是啥?
- 设置想办法让浏览器能够支持下载我们需要的东西;
- 获取下载文件的输入流;
- 创建缓冲区;
- 获取OutputStream对象;
- 将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区;
- 使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端!
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 |
|
3.验证码功能
- 验证怎么来的?
- 前端实现;
- 后端实现,需要用到 Java 的图片类,生产一个图片。
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
4、实现重定向
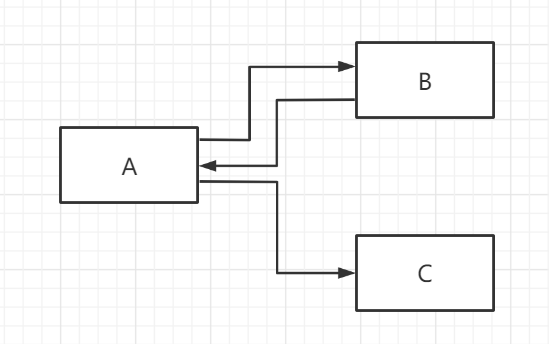
- B一个web资源收到客户端A请求后,B他会通知A客户端去访问另外一个web资源C,这个过程叫
重定向。
常见场景:
- 用户登录
1 | void sendRedirect(String var1) throws IOException; |
- 测试:
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
面试题:请你聊聊重定向和转发的区别?
- 相同点:页面都会实现跳转;
- 不同点:
- 请求转发的时候,url不会产生变化;
- 重定向时候,url地址栏会发生变化;
5.简单实现登录重定向
1 | <%-- |
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> |
7.HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletRequest代表客户端的请求,用户通过Http协议访问服务器,HTTP请求中的所有信息会被封装到HttpServletRequest,通过这个HttpServletRequest的方法,获得客户端的所有信息;
获取参数,请求转发:
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
五、Cookie.Session
1.会话
会话:用户打开一个浏览器,点击了很多超链接,访问多个web资源,关闭浏览器,这个过程可以称之为会话;
有状态会话:一个同学来过教室,下次再来教室,我们会知道这个同学,曾经来过,称之为有状态会话;
你能怎么证明你是西开的学生?
1 | 你 西开 |
一个网站,怎么证明你来过?
1 | 客户端 服务端 |
2.保存会话的两种技术
cookie
- 客户端技术 (响应,请求)
session
- 服务器技术,利用这个技术,可以保存用户的会话信息? 我们可以把信息或者数据放在Session中!
常见常见:网站登录之后,你下次不用再登录了,第二次访问直接就上去了!
3.Cookie
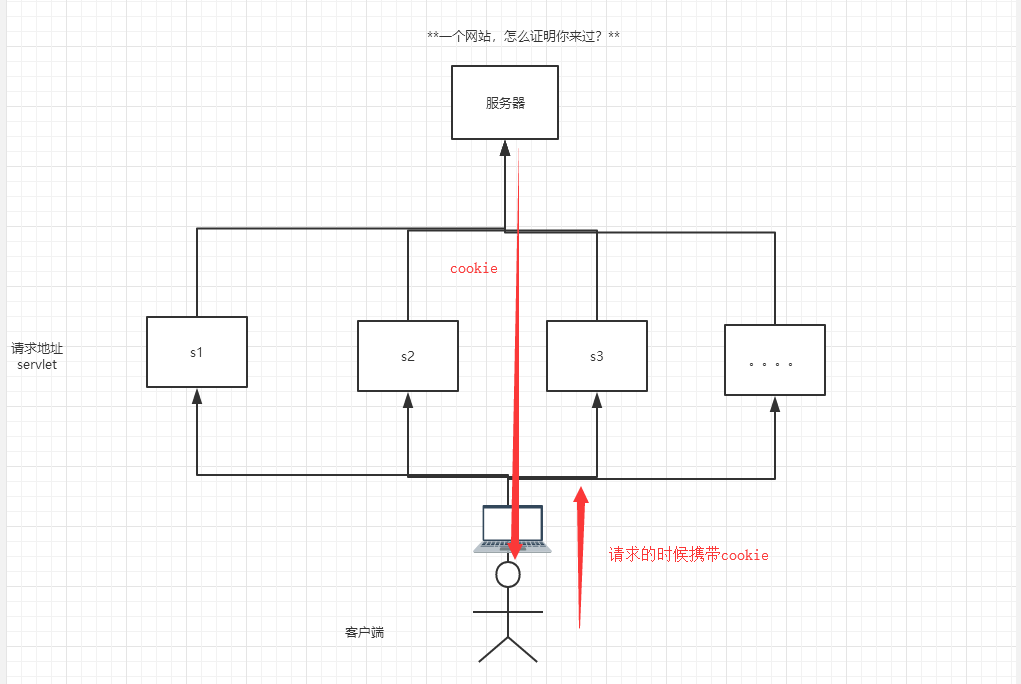
- 从请求中拿到cookie信息;
- 服务器响应给客户端cookie;
1 | Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies(); // 获得Cookie |
- cookie:一般会保存在本地的 用户目录下 appdata;
- 案例:
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
一个网站cookie是否存在上限!聊聊细节问题。
- 一个Cookie只能保存一个信息;
- 一个web站点可以给浏览器发送多个cookie,最多存放20个cookie;
- Cookie大小有限制4kb;
- 300个cookie浏览器上限。
删除Cookie;
- 不设置有效期,关闭浏览器,自动失效;
- 设置有效期时间为 0 ;
编码解码:
1 | URLEncoder.encode("哇哈哈","utf-8") |
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
4.Session(重点)
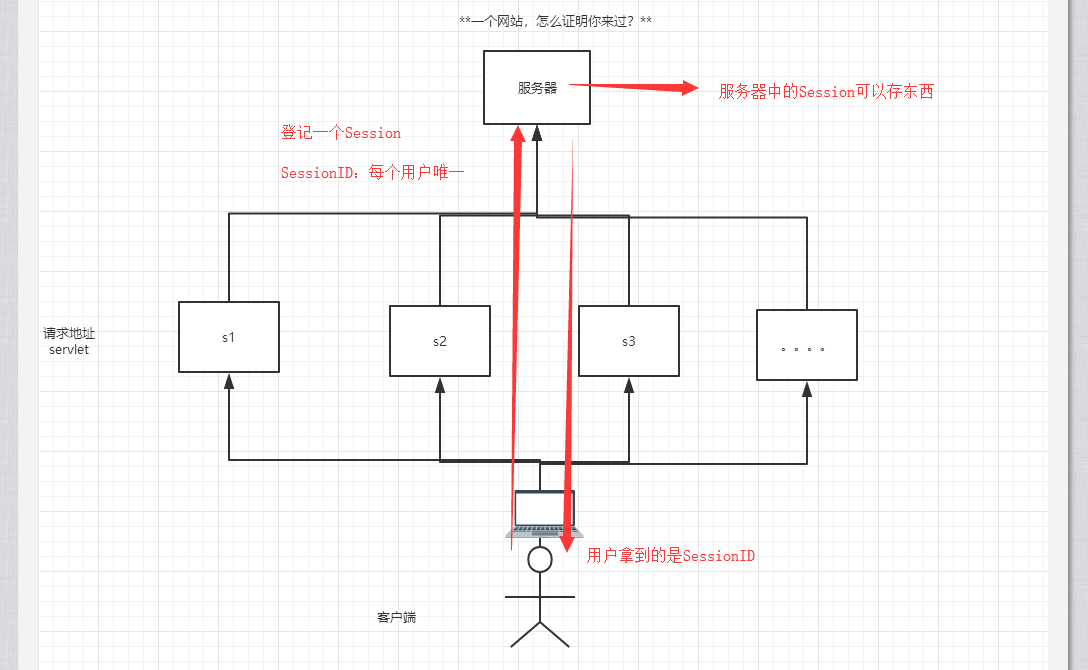
什么是Session:
- 服务器会给每一个用户(浏览器)创建一个Seesion对象;
- 一个Seesion独占一个浏览器,只要浏览器没有关闭,这个Session就存在;
- 用户登录之后,整个网站它都可以访问!–> 保存用户的信息;保存购物车的信息…..
Session和cookie的区别:
- Cookie是把用户的数据写给用户的浏览器,浏览器保存 (可以保存多个)
- Session把用户的数据写到用户独占Session中,服务器端保存 (保存重要的信息,减少服务器资源的浪费)
- Session对象由服务创建;
使用场景:
- 保存一个登录用户的信息;
- 购物车信息;
- 在整个网站中经常会使用的数据,我们将它保存在Session中;
使用Session:
1 | package com.github.pojo; |
1 | package com.github.servlet; |
1 | <servlet> |
会话自动过期:web.xml配置!
1 | <!--设置Session默认的失效时间--> |
1.什么是JSP
Java Server Pages : Java服务器端页面,也和Servlet一样,用于动态Web技术!
- 最大的特点:
- 写JSP就像在写HTML;
- 区别:
- HTML只给用户提供静态的数据;
- JSP页面中可以嵌入JAVA代码,为用户提供动态数据;
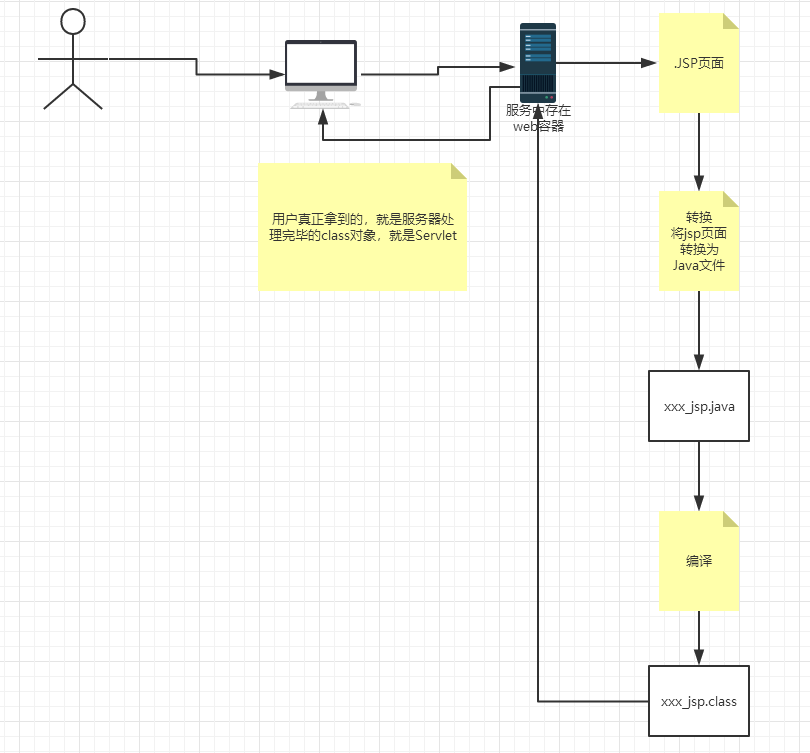
2.JSP原理
思路:JSP到底怎么执行的!
代码层面没有任何问题;
服务器内部工作:
- tomcat中有一个work目录;
IDEA中使用Tomcat的会在IDEA的tomcat中生产一个work目录;
浏览器向服务器发送请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet!
JSP最终也会被转换成为一个Java类!
JSP 本质上就是一个Servlet!
1 | // 初始化 |
判断请求;
内置一些对象;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; // 页面上下文
javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null; // session
final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; // applicationContext
final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; // config
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; // out
final java.lang.Object page = this; // page:当前
HttpServletRequest request // 请求
HttpServletResponse response // 响应输出页面前增加的代码;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9response.setContentType("text/html"); // 设置响应的页面类型
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;以上的这些个对象我们可以在JSP页面中直接使用!
- 在JSP页面中:
- 只要是 JAVA代码就会原封不动的输出;
- 如果是HTML代码,就会被转换为:
1 | out.write("<html>\n"); |
- 这样的格式,输出到前端!
3.JSP基础语法
- 任何语言都有自己的语法,JAVA中有,JSP 作为java技术的一种应用,它拥有一些自己扩充的语法(了解,知道即可!),Java所有语法都支持!
- 配置必需的maven环境:
1 |
|
JSP表达式**
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
jsp脚本片段
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- 脚本片段的再实现
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
JSP声明
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
JSP声明:会被编译到JSP生成Java的类中!其他的,就会被生成到_jspService方法中!
在JSP,嵌入Java代码即可!
1 | <%%> |
- JSP的注释,不会在客户端显示,HTML就会!
4.JSP指令
404与500页面实现
- jsp2.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- 404.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> |
- 500.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> |
- web.xml
1 |
|
头部和尾部页面拼接
- footer.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- header.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- jsp3.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
5.9大内置对象
- PageContext 存东西
- Request 存东西
- Response
- Session 存东西
- Application 【SerlvetContext】 存东西
- config 【SerlvetConfig】
- out
- page ,不用了解
- exception
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
如果EL表达式不生效,请在JSP页面最上面加上:<%@page isELIgnored=”false” %>
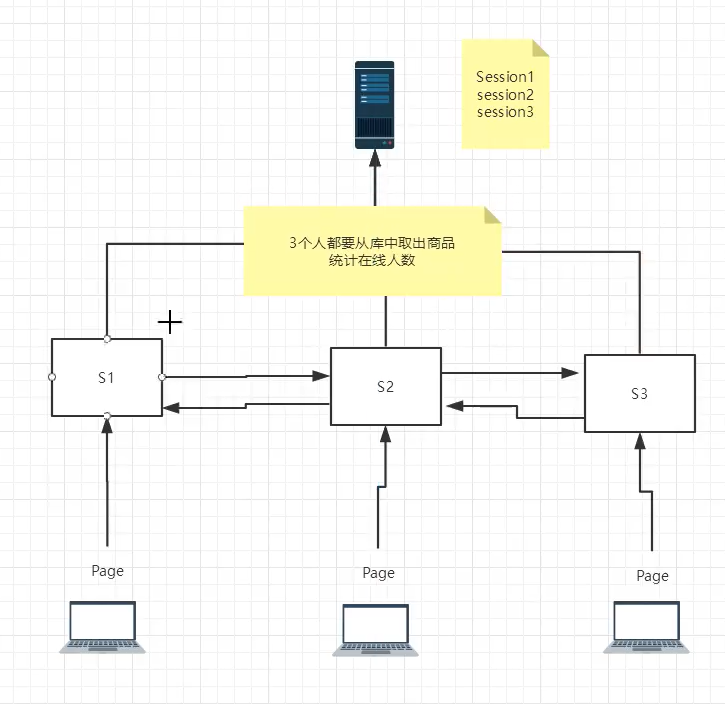
- request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,比如:新闻,用户看完没用的!
- session:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户用完一会还有用,比如:购物车;
- application:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户用完了,其他用户还可能使用,比如:聊天数据;
6.JSP标签.JSTL标签.EL表达式
- EL表达式: ${ }
- 获取数据
- 执行运算
- 获取web开发的常用对象
1 | <!-- JSTL表达式的依赖 --> |
JSP标签
jspTag.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- jspTag2.jsp
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- JSTL表达式
- JSTL标签库的使用就是为了弥补HTML标签的不足;它自定义许多标签,可以供我们使用,标签的功能和Java代码一样!
- 格式化标签
- SQL标签
- XML 标签
- 核心标签 (掌握部分)
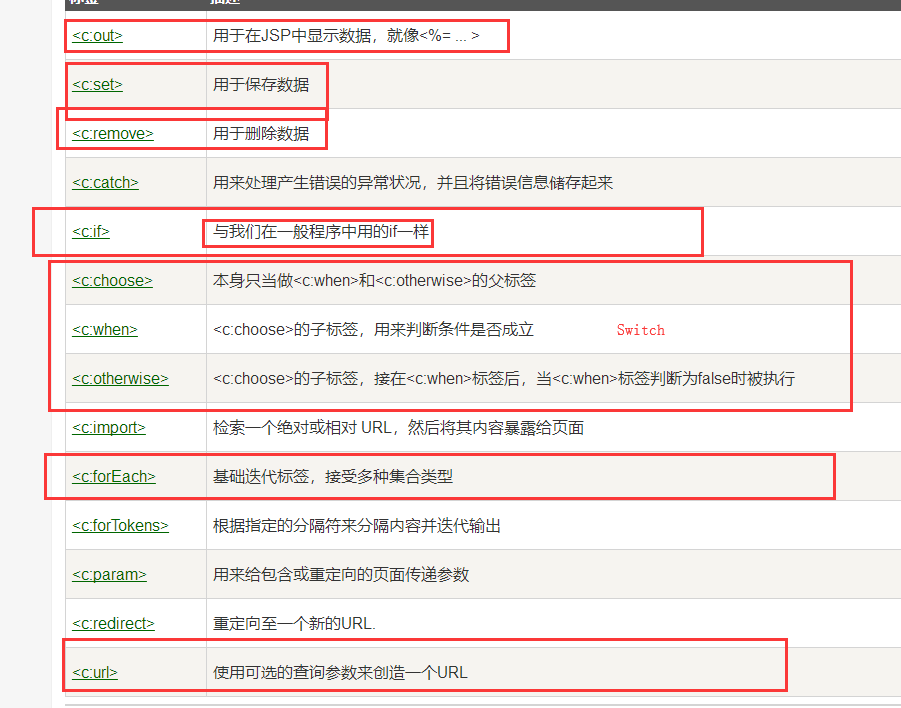
JSTL标签库使用步骤:
- 引入对应的 taglib;
- 使用其中的方法;
- 在Tomcat 的lib目录下也需要引入 jstl-api-1.2.jar、standard-1.1.2.jar的包,否则会报错:JSTL解析错误;
c:if
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- c:choose c:when
1 | <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %> |
- c:forEach
1 | <%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %> |